Amazon Translate is a text translation service that uses advanced machine learning technologies to provide high-quality translation on demand. You can use Amazon Translate to translate unstructured text documents or to build applications that work in multiple languages.
Amazon Translate is a neural machine translation service that delivers fast, high-quality, and affordable language translation.
Amazon Translate can automatically detect the language used in your source text. To use automatic language detection, specify auto as the source language. Amazon Translate calls Amazon Comprehend on your behalf to determine the language used in the source text.
Table of Content
- Use Cases of Amazon Translate
- Supported Formats for the Input Content
- Getting Started (Console)
- Translation Processing Modes
- How Amazon Translate Works with IAM
- Allow Access to the Amazon Translate Console
- AWS Managed Policy: TranslateFullAccess
- AWS Managed Policy: TranslateReadOnly
- Permissions for Using Customer Managed Keys with Custom Terminologies
- Conclusion
Use cases of Amazon Translate
- Translate company-authored content, such as meeting minutes, technician reports, knowledge-base articles, posts, and more.
- Translate interpersonal communications, such as email, in-game chat, customer service chat, so that customers and employees can connect in their preferred language.
- Use the Amazon Translate service to translate content from a source language (the language of the input content) to a target language (the language that you select for the translation output). In a batch job, you can translate files from one or more source languages to one or more target languages.
Supported formats for the input content
One input file – A file containing plain text (.txt), HTML (.html), or Word (.docx) content. Amazon Translate provides the output content as a file in the same format as the input file.
You can use the following features to customize the translations that you produce with Amazon Translate:
- Do-not-translate tags – Uses start and end tags to specify content that you don’t want to translate (in HTML content). For HTML content, you can add do-not-translate tags to text that you don’t want to translate.
<p>In French, the Louvre Museum is <span translate="no">Musée du Louvre</span>.</p> # Add this in source code.
- Custom terminology – Defines how you want Amazon Translate to translate specific terms, such as brand names.
import boto3
translate = boto3.client(service_name='translate')
print("Translating 'Hello' from English to French with the 'Amazon_Family' custom terminology...")
response = translate.translate_text(Text="Hello", TerminologyNames=["Amazon_Family"], SourceLanguageCode="en", TargetLanguageCode="fr")
print("Translated text: " + response.get('TranslatedText'))
print("\n")
- Brevity – Reduces the length of the translation output for most translations (compared to the translation output without brevity). Brevity is supported for real-time text translations.
- Console – In the Text tab of the Real-time translation page, under Additional settings, choose the Brevity setting.
- Profanity – Masks profane words and phrases in your translation output.
- On the Real-time translation page in the Amazon Translate console, under Additional settings, enable the Profanity setting.
- Formality – Sets the level of language formality in your translation output.
- On the Real-time translation page in the Amazon Translate console, under Additional settings, enable the Formality setting and select one of the values.
- Parallel data – Adapts the translation output to reflect the style, tone, and word choices in the example translation samples that you provide.
Getting started (console)
- The easiest way to get started with Amazon Translate is to use the console to translate some text. You can translate up to 10,000 bytes of text using the console.
- Open the Amazon Translate console
- If this is the first time that you’ve used Amazon Translate, choose Launch real-time translation.
- In Real-time translation, choose the target language.
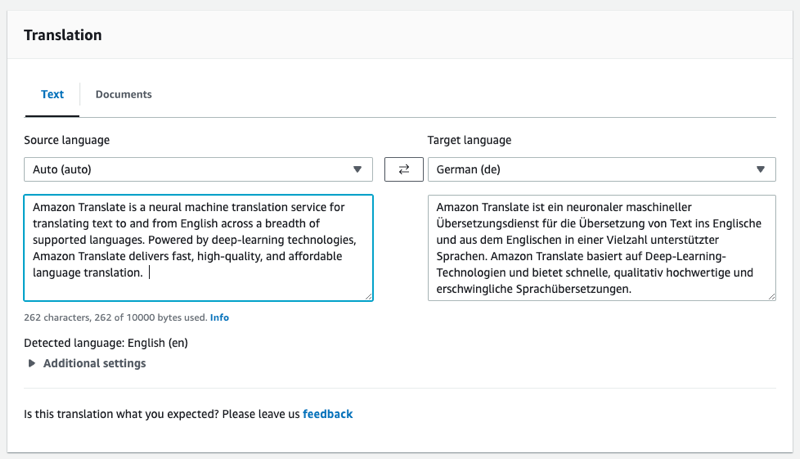
- In the Application integration section you can see the JSON input and output for the TranslateText operation.

Translation processing modes
- Real-time translation – You make a synchronous request to translate a small amount of text (or a text file) and Amazon Translate responds immediately with the translated text.
- Open the Amazon Translate console.
- In the navigation menu on the left, choose Real-time translation.
- For Source language, select the language of the source text, or keep the value as Auto for auto detection.
- For Target language, select a language.
- Enter or paste text into the Source language text box. The console displays the translated text in the Target language text box.
- Asynchronous batch processing – You put a collection of documents in an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) location and start an asynchronous processing job to translate them. Amazon Translate sends the translated output documents to a specified Amazon S3 location.
To perform an asynchronous batch translation, you typically perform the following steps:
- Store a set of documents in an input folder inside of an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Start a batch translation job.
- As part of your request, provide Amazon Translate with an IAM role that has read access to the input Amazon S3 folder and all its sub-folders. The role must also have read and write access to an output Amazon S3 bucket.
IAM role policy to get and put objects from Buckets
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::input-bucket-name/*",
"arn:aws:s3:::output-bucket-name/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:ListBucket",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::input-bucket-name",
"arn:aws:s3:::output-bucket-name"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::output-bucket-name/*"
}
]
}
The following trust policy allows Amazon Translate to assume the IAM role that the policy belongs to.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "translate.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"ArnLike": {
"aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:translate:*:111122223333:*"
},
"StringEquals": {
"aws:SourceAccount": "111122223333"
}
}
}
]
}
Example KMS key policy statement to allow an IAM role to use the key
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal":
{
"AWS":
[
"arn:aws:iam::444455556666:role/AmazonTranslateServiceRoleS3FullAccess",
"arn:aws:iam::444455556666:admin"
]
},
"Action":
[
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:CreateGrant",
"kms:GenerateDataKey",
"kms:RetireGrant",
"kms:DescribeKey"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
- Monitor the progress of the batch translation job.
- Retrieve the results of the batch translation job from the specified output bucket.
How Amazon Translate works with IAM
Allow access to the Amazon Translate console
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"iam:ListRoles",
"iam:GetRole",
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
AWS managed policy: TranslateFullAccess
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"translate:*",
"comprehend:DetectDominantLanguage",
"cloudwatch:GetMetricStatistics",
"cloudwatch:ListMetrics",
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"iam:ListRoles",
"iam:GetRole"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
AWS managed policy: TranslateReadOnly
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"translate:TranslateText",
"translate:TranslateDocument",
"translate:GetTerminology",
"translate:ListTerminologies",
"translate:ListTextTranslationJobs",
"translate:DescribeTextTranslationJob",
"translate:GetParallelData",
"translate:ListParallelData",
"comprehend:DetectDominantLanguage",
"cloudwatch:GetMetricStatistics",
"cloudwatch:ListMetrics"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
permissions for using customer managed keys with custom terminologies
{
"Id": "key-consolepolicy-3",
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Allow access for use with Amazon Translate",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "IAM USER OR ROLE ARN"
},
"Action": [
"kms:CreateAlias",
"kms:CreateGrant",
"kms:DescribeKey",
"kms:GenerateDataKey",
"kms:GetKeyPolicy",
"kms:PutKeyPolicy",
"kms:RetireGrant"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Conclusion
In this article you learned everything about Amazon Translate

