AWS Control tower helps to manage and setup multi account environment. AWS Control Tower orchestrates the capabilities of several other AWS services, including AWS Organizations, AWS Service Catalog, and AWS IAM Identity Center, to build a landing zone in less than an hour.

Note: A landing zone is a well-architected, multi-account AWS environment that is scalable and secure. This is a starting point from which your organization can quickly launch and deploy workloads and applications with confidence in your security and infrastructure environment.
To help keep your organizations and accounts from drift, which is divergence from best practices, AWS Control Tower applies controls (sometimes called guardrails). For example, you can use controls to help ensure that security logs and necessary cross-account access permissions are created, and not altered
If you modify AWS Control Tower resources, such as an SCP, or remove any AWS Config resource, such as a Config recorder or aggregator, AWS Control Tower can no longer guarantee that the controls are functioning as designed.
When you go through the setup process, AWS Control Tower launches a key resource associated with your account, called a landing zone, which serves as a home for your organizations and their accounts.
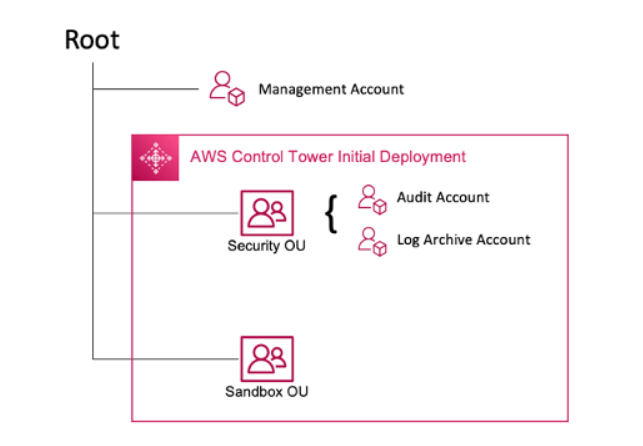
Table of Content
- AWS Control Tower Features and Terminologies
- Structure of an AWS Control Tower Landing Zone
- AWS Control Tower Pricing
- Management Account
- Member Accounts
- Methods to Create or Update Member Account
- How AWS Control Tower Creates an Account
- Working of AWS Control Tower
- Steps to Setup Landing Zone with AWS Control Tower API
- Creating AWS Control Tower with Console
- Updating the Landing Zone with AWS Control Tower
- Listing Landing Zone with AWS Control Tower
- Resolve Drift
- Automate Tasks in AWS Control Tower
- AWS Control Tower and VPCs
- IAM Identity Center Groups for AWS Control Tower
- Roles within AWS Control Tower
- AWSControlTowerStackSetRole
- AWSServiceRoleForAWSControlTower
- AWSControlTowerAdmin Role
- AWSControlTowerExecution Role
AWS Control Tower Features and Terminologies
AWS Control Tower supports and work with:

- Landing Zone is an multi account environment that’s based on security and compliance. It holds all OU’s, accounts, users and other resources.
- Controls also known as Guardrails are high level rules which allows to protect your Amazon account. Three kinds of controls exist: preventive, detective, and proactive.
- Preventive controls prevent actions from occurring. For example, the elective control called Disallow Changes to Bucket Policy for Amazon S3 Buckets.
- Detective controls detect specific events when they occur and log the action in CloudTrail.
- Proactive controls check whether resources are compliant with your company policies and objectives, before the resources are provisioned in your accounts.
- Account Factory is a configurable account template that helps helps to standardize the provisioning of new accounts with pre-approved account configurations.
- The dashboard offers continuous oversight of your landing zone to your team of central cloud administrators.
- An AWS Account Factory account is an AWS account provisioned using Account Factory in AWS Control Tower. Sometimes, Account Factory is referred to informally as a “vending machine” for accounts.
- Your AWS Control Tower home Region is the AWS Region in which your AWS Control Tower landing zone was deployed.
- AWS Service Catalog allows you to manage commonly deployed IT services, centrally.
- A baseline in AWS Control Tower is a group of resources and specific configurations that you can apply to a target.
- A stack instance is a reference to a stack in a target account within a Region.
- A stack is a collection of AWS resources that you can manage as a single unit.
- IAM Identity Center can be installed only in the management account of an organization.
AWS Control Tower allows you to customize new and existing AWS accounts when you provision their resources from the AWS Control Tower console. After you set up account factory customization, AWS Control Tower automates this process for future provisioning, so you don’t have to maintain any pipelines. Customized accounts are available for use immediately after the resources are provisioned.

Structure of an AWS Control Tower Landing Zone
When you set up a landing zone, AWS Control Tower performs the following actions in your management account on your behalf:
- Root – The parent that contains all other OUs in your landing zone.
- Security OU – This OU contains the Log Archive and Audit accounts.
- Sandbox OU – The Sandbox OU is created when you launch your landing zone, if you enable it.
- IAM Identity Center directory – This directory houses your IAM Identity Center users. It defines the scope of permissions for each IAM Identity Center user.
- IAM Identity Center users – These are the identities that your users can assume to perform their AWS workloads in your landing zone.
Note: In AWS Control Tower, the shared accounts in your landing zone are provisioned during setup: the management account, the log archive account, and the audit account.
When you set up a landing zone, AWS Control Tower performs the following actions in your management account on your behalf:
- Creates two AWS Organizations organizational units (OUs): Security, and Sandbox (optional), contained within the organizational root structure.
- Creates or adds two shared accounts in the Security OU: the Log Archive account and the Audit account.
- Creates a cloud-native directory in IAM Identity Center, with preconfigured groups and single sign-on access, if you choose the default AWS Control Tower configuration, or it allows you to self-manage your identity provider.
- Preventive controls are not applied to the management account.
- Except for the management account, controls are applied to the organization as a whole.
AWS Control Tower Pricing
No additional charge exists for using AWS Control Tower. You only pay for the AWS services enabled by AWS Control Tower, and the services you use in your landing zone.
Management Account
Management account is the account that you created specifically for your landing zone. This account is used for billing for everything in your landing zone. It’s also used for Account Factory provisioning of accounts, as well as to manage OUs and controls.
This AWS account launches AWS Control Tower. By default, the root user for this account and the IAM user or IAM administrator user for this account have full access to all resources within your landing zone.
Member accounts
Member accounts are the accounts through which your users perform their AWS workloads. These member accounts can be created in Account Factory, by IAM Identity Center users with Admin privileges in the Service Catalog console, or by automated methods. When created, these member accounts exist in an OU that was created in the AWS Control Tower console, or registered with AWS Control Tower.
Methods to Create or Update Member Account
AWS Control Tower provides several methods for creating and updating member accounts. Some methods are primarily console-based, and some methods are primarily automated.
- You can customize accounts during provisioning, in a GitOps-style workflow, with Account Factory for Terraform (AFT).AFT is deployed with a Terraform module, available in the AFT repository.
- You can customize your AWS Control Tower landing zone with Customizations for AWS Control Tower (CfCT), a package of functionality that is built upon AWS CloudFormation templates and service control policies (SCPs).
- The standard way to create member accounts is through Account Factory, a console-based product that’s part of the Service Catalog. In the AWS Control Tower console, you can use Account Factory to create, update, or enroll up to five accounts at the same time.
- From your AWS Control Tower landing zone’s management account, using Lambda code and appropriate IAM roles.
- Through the Enroll account feature within AWS Control Tower, if your landing zone is not in a state of drift.
- From the AWS Control Tower Account Factory for Terraform (AFT), which relies on Account Factory and a GitOps model to allow automation of account provisioning and updating.
- Accounts are provisioned by means of a AWS Service Catalog product called a blueprint. A blueprint can use AWS CloudFormation templates, or Terraform templates.
How AWS Control Tower creates an account
- You initiate the request, for example, from the AWS Control Tower Account Factory page, or directly from the AWS Service Catalog console, or by calling the Service Catalog
ProvisionProductAPI. - AWS Service Catalog calls AWS Control Tower.
- AWS Control Tower begins a workflow, which as a first step calls the AWS Organizations
CreateAccountAPI. - After AWS Organizations creates the account, AWS Control Tower completes the provisioning process by applying blueprints and controls.
- Service Catalog continues to poll AWS Control Tower to check for completion of the provisioning process.
- When the workflow in AWS Control Tower is complete, Service Catalog finalizes the account’s state and informs you (the requester) of the result.
Working of AWS Control Tower
AWS Control Tower uses AWS CloudFormation StackSets to set up resources in your accounts. Each stack set has StackInstances that correspond to accounts, and to AWS Regions per account. AWS Control Tower deploys one stack set instance per account and Region.
Steps to Setup Landing Zone with AWS Control Tower API
Before AWS Control Tower sets up the landing zone, it automatically runs a series of pre-launch checks in your account. The process of setting up your AWS Control Tower landing zone is as followed:
- Create your shared account email addresses.
- Perform the configuration and launch of your landing zone.
- Configure your shared accounts, logging, and encryption
- Creating an IAM role or IAM Identity Center user with the required permissions to call the landing zone APIs.
- Creating a new AWS Organizations organization.
- Call the AWS Control Tower CreateLandingZone API.
- Create your shared account email addresses. Setting up your shared account email addresses.
aws organizations create-account --email mylog@example.com --account-name "Logging Account"
aws organizations create-account --email mysecurity@example.com --account-name "Security Account"
- Perform the landing zone configuration. Configure and launch your landing zone.
- Customize the log retention policy for Amazon S3 buckets that store your AWS CloudTrail logs in AWS Control Tower, in increments of days or years, up to a maximum of 15 years.
- Select the home region.
- select whether AWS Control Tower sets up AWS account access with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), or whether to self-manage AWS account access—either with AWS IAM Identity Center users, roles, and permissions that you can set up and customize on your own, or with another method such as an external IdP.
- AWS Control Tower to set up an organization-level CloudTrail trail and manage it for you, choose Opt in.
- If you wish to encrypt and decrypt your resources with an AWS KMS encryption key. The KMS key policy would be.
{
"Sid": "Allow Config to use KMS for encryption",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "config.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:GenerateDataKey"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:kms:YOUR-HOME-REGION:YOUR-MANAGEMENT-ACCOUNT-ID:key/YOUR-KMS-KEY-ID"
}
- Creating an IAM role or IAM Identity Center user with the required permissions to call the landing zone APIs. Create the following IAM service roles that enable AWS Control Tower to perform the API calls required to set up your landing zone:
Create an IAM role with the necessary permissions to call all landing zone APIs.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"controltower:CreateLandingZone",
"controltower:UpdateLandingZone",
"controltower:ResetLandingZone",
"controltower:DeleteLandingZone",
"controltower:GetLandingZoneOperation",
"controltower:GetLandingZone",
"controltower:ListLandingZones",
"controltower:ListTagsForResource",
"controltower:TagResource",
"controltower:UntagResource",
"servicecatalog:*",
"organizations:*",
"sso:*",
"sso-directory:*",
"logs:*",
"cloudformation:*",
"kms:*",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:GetSAMLProvider",
"iam:CreateSAMLProvider",
"iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole",
"iam:ListRolePolicies",
"iam:PutRolePolicy",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DeleteRolePolicy",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
The existing service limits for the AWS account must be sufficient for AWS Control Tower to launch. The AWS account must be subscribed to the following AWS services:
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2)
- Amazon SNS
- Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC)
- AWS CloudFormation
- AWS CloudTrail
- Amazon CloudWatch
- AWS Config
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- AWS Lambda
You can set up an AWS Control Tower landing zone in an existing organization, or you can start by creating a new organization that contains your AWS Control Tower landing zone.
- Creating a new AWS Organizations organization.
aws organizations create-organization --feature-set ALL
- Call the AWS Control Tower
CreateLandingZoneAPI. This API requires a landing zone version and a manifest file as input.
aws controltower create-landing-zone --landing-zone-version 3.3 --manifest "file://LandingZoneManifest.json"
- landingzonemainfest.json
{
"governedRegions": ["us-west-2","us-west-1"],
"organizationStructure": {
"security": {
"name": "CORE"
},
"sandbox": {
"name": "Sandbox"
}
},
"centralizedLogging": {
"accountId": "222222222222",
"configurations": {
"loggingBucket": {
"retentionDays": 60
},
"accessLoggingBucket": {
"retentionDays": 60
},
"kmsKeyArn": "arn:aws:kms:us-west-1:123456789123:key/e84XXXXX-6bXX-49XX-9eXX-ecfXXXXXXXXX"
},
"enabled": true
},
"securityRoles": {
"accountId": "333333333333"
},
"accessManagement": {
"enabled": true
}
}
Creating AWS Control Tower with Console
- Sign in to the AWS management console and navigate to the AWS Control Tower console.
- Verify that you are working in your desired home Region.
- To set up your landing zone with new shared accounts, AWS Control Tower requires two unique email addresses that aren’t already associated with an AWS account. The email addresses are required for Audit account and Log archive account.
- Choose Set up landing zone.
- Accept all the default values. You will need to type in the email address for your account, a log archive account, and an audit account.
- Confirm your choices and choose Set up landing zone.
- AWS Control Tower takes about 30 minutes to set up all of the resources in your landing zone.
Updating the landing zone with AWS Control Tower
The easiest way to update your AWS Control Tower landing zone is through the Landing zone settings page, which you can reach by choosing Landing zone settings in the left navigation of the AWS Control Tower dashboard.
To update your landing zone manually, with any number of accounts per OU
- Open a web browser, and navigate to the AWS Control Tower console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/controltower/home/update.
- Review the information in the wizard and choose Update. This updates the backend of the landing zone as well as your shared accounts. This process can take a little more than half an hour.
- Update your member accounts (this procedure must be followed for an OU that contains over 300 accounts).
- From the left navigation pane, choose Organization.
- To update each account, follow the steps given in Update the account in the console.
aws controltower update-landing-zone --landing-zone-version 3.3 --landing-zone-identifier "arn:aws:controltower:us-west-2:123456789123:landingzone/1A2B3C4D5E6F7G8H" --manifest file://LandingZoneManifest.json
Listing Landing Zone with AWS Control Tower
aws controltower list-landing-zones --region us-east-1
Resolve Drift
Drift often occurs as you and your organization members use the landing zone. Drift detection is automatic in AWS Control Tower. Automated scans of your SCPs help you identify resources that need changes or configuration updates that must be made to resolve the drift. To repair most types of drift, choose Reset on the Landing zone settings page.
You can provision or update individual accounts in AWS Control Tower by several methods:
- You can provision and customize accounts with AWS Control Tower Account Factory for Terraform (AFT).
- Account Factory for Terraform (AFT) sets up a Terraform pipeline to help you provision and customize accounts in AWS Control Tower. AFT provides you with the advantage of Terraform-based account provisioning while allowing you to govern your accounts with AWS Control Tower.
- You can update accounts with Customizations for AWS Control Tower (CfCT). Customizations for AWS Control Tower (CfCT) are deployed in your management account after you launch your AWS CloudFormation template.
- If you prefer to use an API approach, you can update accounts using the API framework of Service Catalog and the AWS CLI to update the accounts in a batch process.
Automate tasks in AWS Control Tower
Many customers prefer to automate tasks in AWS Control Tower, such as account provisioning, control assignment, and auditing. You can set up these automated actions with calls to:
- AWS Service Catalog APIs
- AWS Organizations APIs
- AWS Control Tower APIs
- AWS CLI
AWS Control Tower and VPCs
Here are some essential facts about AWS Control Tower VPCs:
- The VPC created by AWS Control Tower when you provision an account in Account Factory is not the same as the AWS default VPC.
- When AWS Control Tower sets up a new account in a supported AWS Region, AWS Control Tower automatically deletes the default AWS VPC, and it sets up a new VPC configured by AWS Control Tower.
- Each AWS Control Tower account is allowed one VPC that’s created by AWS Control Tower. An account can have additional AWS VPCs within the account limit.
IAM Identity Center Groups for AWS Control Tower
| Account | Permission sets | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Management account | AWSServiceCatalogEndUserAccess | This group is only used in this account to provision new accounts using Account Factory. |
| Account | Permission sets | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Management account | AWSAdministratorAccess | Users of this group in this account are the only ones that have access to the AWS Control Tower console. |
| Log archive account | AWSAdministratorAccess | Users have administrator access in this account. |
| Audit account | AWSAdministratorAccess | Users have administrator access in this account. |
| Member accounts | AWSOrganizationsFullAccess | Users have full access to Organizations in this account. |
AWSControlTowerStackSetRole
AWS CloudFormation assumes this role to deploy stack sets in accounts created by AWS Control Tower.
AWSServiceRoleForAWSControlTower
This role provides AWS Control Tower with access to the Log Archive account, Audit account, and member accounts, for operations critical to maintaining the landing zone, such as notifying you of drifted resources.
The AWSServiceRoleForAWSControlTower role requires an attached managed policy and a role trust policy for the IAM role.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "controltower.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Managed policy for this role: AWSControlTowerAccountServiceRolePolicy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
//For creating the managed rule
"Sid": "AllowPutRuleOnSpecificSourcesAndDetailTypes",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "events:PutRule",
"Resource": "arn:aws:events:*:*:rule/*ControlTower*",
"Condition": {
"ForAnyValue:StringEquals": {
"events:source": "aws.securityhub"
},
"Null": {
"events:detail-type": "false"
},
"StringEquals": {
"events:ManagedBy": "controltower.amazonaws.com",
"events:detail-type": "Security Hub Findings - Imported"
}
}
},
// Other operations to manage the managed rule
{
"Sid": "AllowOtherOperationsOnRulesManagedByControlTower",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"events:DeleteRule",
"events:EnableRule",
"events:DisableRule",
"events:PutTargets",
"events:RemoveTargets"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:events:*:*:rule/*ControlTower*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"events:ManagedBy": "controltower.amazonaws.com"
}
}
},
// More managed rule permissions
{
"Sid": "AllowDescribeOperationsOnRulesManagedByControlTower",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"events:DescribeRule",
"events:ListTargetsByRule"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:events:*:*:rule/*ControlTower*"
},
// Add permission to publish the security notifications to SNS
{
"Sid": "AllowControlTowerToPublishSecurityNotifications",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sns:publish",
"Resource": "arn:aws:sns:*:*:aws-controltower-AggregateSecurityNotifications",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:PrincipalAccount": "${aws:ResourceAccount}"
}
}
},
// For drift verification
{
"Sid": "AllowActionsForSecurityHubIntegration",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"securityhub:DescribeStandardsControls",
"securityhub:GetEnabledStandards"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:securityhub:*:*:hub/default"
}
]
}
AWSControlTowerAdmin role
This role provides AWS Control Tower with access to infrastructure critical to maintaining the landing zone. The AWSControlTowerAdmin role requires an attached managed policy and a role trust policy for the IAM role. A role trust policy is a resource-based policy, specifying which principals can assume the role.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "controltower.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
This role requires two IAM policies.
- An inline policy, for example:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
- The managed policy that follows, which is the
AWSControlTowerServiceRolePolicy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:CreateStackInstances",
"cloudformation:CreateStackSet",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStackInstances",
"cloudformation:DeleteStackSet",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackInstance",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackSet",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackSetOperation",
"cloudformation:ListStackInstances",
"cloudformation:UpdateStack",
"cloudformation:UpdateStackInstances",
"cloudformation:UpdateStackSet"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:*:type/resource/AWS-IAM-Role"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"account:EnableRegion",
"account:ListRegions",
"account:GetRegionOptStatus"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:CreateStackInstances",
"cloudformation:CreateStackSet",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStackInstances",
"cloudformation:DeleteStackSet",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackInstance",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackSet",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackSetOperation",
"cloudformation:GetTemplate",
"cloudformation:ListStackInstances",
"cloudformation:UpdateStack",
"cloudformation:UpdateStackInstances",
"cloudformation:UpdateStackSet"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:*:stack/AWSControlTower*/*",
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:*:stack/StackSet-AWSControlTower*/*",
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:*:stackset/AWSControlTower*:*",
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:*:stackset-target/AWSControlTower*/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudtrail:CreateTrail",
"cloudtrail:DeleteTrail",
"cloudtrail:GetTrailStatus",
"cloudtrail:StartLogging",
"cloudtrail:StopLogging",
"cloudtrail:UpdateTrail",
"cloudtrail:PutEventSelectors",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents",
"logs:PutRetentionPolicy"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:logs:*:*:log-group:aws-controltower/CloudTrailLogs:*",
"arn:aws:cloudtrail:*:*:trail/aws-controltower*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::aws-controltower*/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/AWSControlTowerExecution",
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/AWSControlTowerBlueprintAccess"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudtrail:DescribeTrails",
"ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones",
"iam:ListRoles",
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:DescribeLogGroups",
"organizations:CreateAccount",
"organizations:DescribeAccount",
"organizations:DescribeCreateAccountStatus",
"organizations:DescribeOrganization",
"organizations:DescribeOrganizationalUnit",
"organizations:DescribePolicy",
"organizations:ListAccounts",
"organizations:ListAccountsForParent",
"organizations:ListAWSServiceAccessForOrganization",
"organizations:ListChildren",
"organizations:ListOrganizationalUnitsForParent",
"organizations:ListParents",
"organizations:ListPoliciesForTarget",
"organizations:ListTargetsForPolicy",
"organizations:ListRoots",
"organizations:MoveAccount",
"servicecatalog:AssociatePrincipalWithPortfolio"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:GetUser",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:GetRolePolicy"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"iam:PassRole"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/service-role/AWSControlTowerStackSetRole",
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/service-role/AWSControlTowerCloudTrailRole",
"arn:aws:iam::*:role/service-role/AWSControlTowerConfigAggregatorRoleForOrganizations"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"config:DeleteConfigurationAggregator",
"config:PutConfigurationAggregator",
"config:TagResource"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:ResourceTag/aws-control-tower": "managed-by-control-tower"
}
}
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"organizations:EnableAWSServiceAccess",
"organizations:DisableAWSServiceAccess"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"organizations:ServicePrincipal": [
"config.amazonaws.com",
"cloudtrail.amazonaws.com"
]
}
}
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:AWSServiceName": "cloudtrail.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
AWSControlTowerExecution role
The AWSControlTowerExecution role must be present in all enrolled accounts. It allows AWS Control Tower to manage your individual accounts and report information about them to your Audit and Log Archive accounts.
AWSControlTowerExecutionallows you to create and enroll accounts, automatically, with scripts and Lambda functions.AWSControlTowerExecutionhelps you configure your organizations’s logging, so that all the logs for every account are sent to the logging account.AWSControlTowerExecutionallows you to enroll an individual account in AWS Control Tower.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"controltower.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:SourceAccount": "012345678901"
},
"StringLike": {
"aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:controltower:us-west-2:012345678901:*"
}
}
}
]
}
Security of AWS Control Tower
AWS Control Tower uses Amazon S3 buckets and Amazon DynamoDB databases that are encrypted at rest by using Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3) in support of your landing zone.
AWS Control Tower uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) and client-side encryption for encryption in transit in support of your landing zone.
Conclusion
In this article you learnt everything about AWS Control Tower.

